
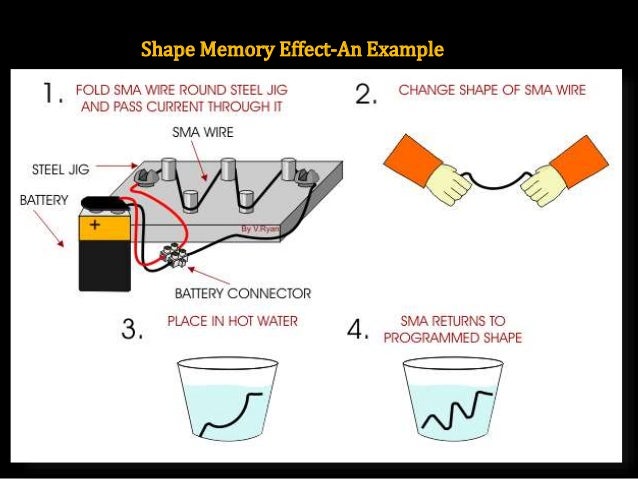
Hydrogels’ ability to absorb large amounts of water without dissolving is due to the chains’ arrangement in a three-dimensional network. Function of Smart materials used in 4D PrintingĬross-linking polymer chains made of hydrophilic monomers form a hydrogel. Fabrication of high-resolution structures that stay stable in both temporary and permanent spatial configurations is another area of increasing attention. Biocompatibility, for example, is a significant concern in the manufacture of biomedical equipment. As a result, the smart material (or a mix of materials) that is selected is completely dependent on the intended use of the final printed item. The physical characteristics of the printing materials may be used to produce a desired stimulus-response in the final printed structure. The materials react by undergoing actuation, which involves shape-morphing or functional alteration, culminating in a structural change. In 4D printing, smart materials play a significant role in receiving, transferring, and analyzing the applied stimuli. The variety of smart materials suitable for printing has grown in recent years as the field has progressed. The purpose of this article is to provide an overview of various 4D printing techniques and their applications in Healthcare, such as drug delivery systems and bioprinting. As 4D Printing may enable the uses of soft robotic technology, such as adaptable sensors and actuators. This article aims to provide a brief overview of the fundamental aspects of 4D printing technologies and advancing biomedical applications. The concept of 4D printing explores a new branch of additive manufacturing research that has the potential to expand the capabilities of both 3D and 4D printing technologies. In medical devices, the growing interest in 4D printing has been studied in responsive structures such as soft robotics and printed actuators. Smart material is at the core of 4D printing technology, as it allows printed products to be more flexible, expandable, and deformable in response to specific stimuli. Custom 4D-printed implants, fixtures, and surgical tools, for example, can reduce the time required for surgery and patient recovery while also increasing the success of the surgery or implant. The use of 4D printing in healthcare allows for the customization and personalization of medical products, drugs, and equipment, which benefits both healthcare providers and patients. As a result, 4D printing can be used to create bones, ears, exoskeletons, windpipes, jawbones, eyeglasses, cell cultures, stern cells, blood vessels, vascular networks, tissues, and organs, as well as novel dosage forms and drug delivery devices. However, because 3D printing outputs are rigid in nature, 4D printing technology’s flexible products allow organ parts to be customized based on a patient’s appearance. The introduction of 3D printing sparked numerous changes in the healthcare industry. This is how a lifeless object changes shape and behavior over time. When hot water, light, or heat is added to smart materials (also known as programmable materials), they exhibit different functionalities. Although printed in the same way as a 3D-printed shape, a 4D-printed device can change over time.
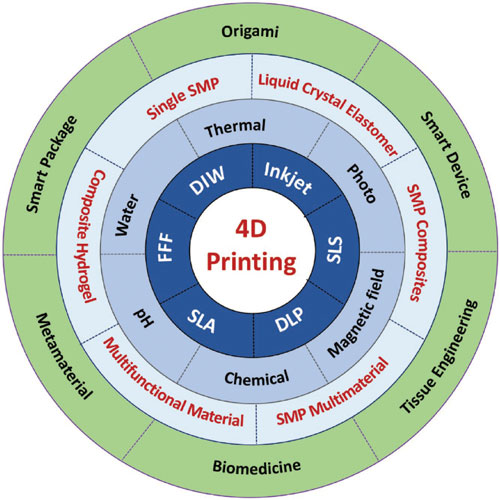
Even though the technology is in the R&D phase, prototypes have been witnessed in various industries, including automotive, medical, and aviation.

Smart materials are used in 4D printing to create objects that can self-assemble, be flexible, and adapt to changing conditions. One such invention is 4D printing, in which the fourth dimension is time. While 3D printing is utilized in a wide variety of sectors, the growing complexity of the materials used has provided an opportunity for technical advancements. 4D Printing technology is rapidly expanding and replacing traditional production in a wide range of industries, including aerospace engineering, automobile, and medical devices. As a result, many pharmaceutical device and formulation concepts that can be printed and possibly tailored to an individual have emerged. Recently, many studies have explored a new field that integrates 3D and 4D printing with therapeutics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
